

NM-16ESW is 16 port switch module (from f1/0 to f1/15). \ios.run\c2600-te.binĭynamips loads ios with NM-16ESW module in slot 1, and listens 30000 to 30002. net file (ether mode), please refer to dynagen for details. The line started with '#' or '!' will be discarded. All the commands in the startup file are the internal command of the VPCS. VPCS looks for the file named 'startup.vpc' in the current directory, and execute the commands in it if you are not set the startup file from the command line. When VPCS started, it listens the ports from 20000 to 20008 and wait the dymamips to connet, and send the packets to the ports from 30000 to 30008 which should be listened by the Dynamips. If in the ether mode, please run it before the dynamips loads/starts the ios. The tapx ip to 10.1.1.126 in the ether mode. The ip of the tapx is the maximum host ID of the subnet.
#VPCS IN GNS3 TUTORIAL PC#
PC will try to get the ipv6 address from the router at startupĪddress CIDR set the PC's ip, gateway's ip and network maskĭefault IPv4 CIDR is 24, IPv6 is 64. Ip address CIDR, Set the PC's ip, gateway's ip and network mask.ĭhcp Configure host/gateway address using DHCP, only ipv4Īuto Stateless address autoconfiguration, only ipv6 w ms wait 'ms' milliseconds to receive the response VPCS> i i ms wait 'ms' milliseconds between sending each packet Ping address, Ping the network host, Ctrl+C to stop the command Version Shortcut for: show version VPCS> sh Trace HOST Print the path packets take to network HOST Sleep Print TEXT and pause running script for seconds Show Print the information of VPCs (default). Save Save the configuration to the file FILENAME Rlogin port Telnet to port on host at ip (relative to host PC) Configure packet relay between UDP ports. Ping HOST Ping HOST with ICMP (default) or TCP/UDP. Load Load the configuration/script from the file FILENAME Get IPv4 address via DHCPĭisconnect Exit the telnet session (daemon mode)Įcho TEXT Display TEXT in output. Show arp tableĬlear ARG Clear IPv4/IPv6, arp/neighbor cache, command historyĭhcp Shortcut for: ip dhcp. digit range 1 to 9Īrp Shortcut for: show arp. ! COMMAND Invoke an OS COMMAND with optional ARG(s)ĭigit Switch to the VPCdigit.
Startup.vpc if it exists in the current directory. If no FILENAME specified, vpcs will read and execute the file named H port run as the hypervisor listening on the tcp port d device device name, works only when -i is set to 1 c port remote udp base port (dynamips udp port), default from 30000 s port local udp base port, default from 20000 e tap mode, using /dev/tapx by default (linux only) FILENAME load and execute script file FILENAME m num start byte of ether address, default from 0 p port run as a daemon listening on the tcp port i num number of vpc instances to start (default is 9) The source tarball was signed by my GPG key E90A5CF0, run gpg –verify to verify:
#VPCS IN GNS3 TUTORIAL CODE#
The source code was released under BSD license, download from sourceforge. The Simplified Chinese user guide, download from sourceforge. And special thanks to Chris Welsh for his suggestions and help. The stable version 0.8a, download from sourceforge, has been tested under FreeBSD/Linux/OSX/Windows, changelog.

In the ether mode, via /dev/tap, not support In the udp mode, VPCS sends or receives the packets via udp. Now, VPCS can be run in udp or ether mode. VPCS can replace the routers or VMware boxes which are used as PCs in the Dynamips network.
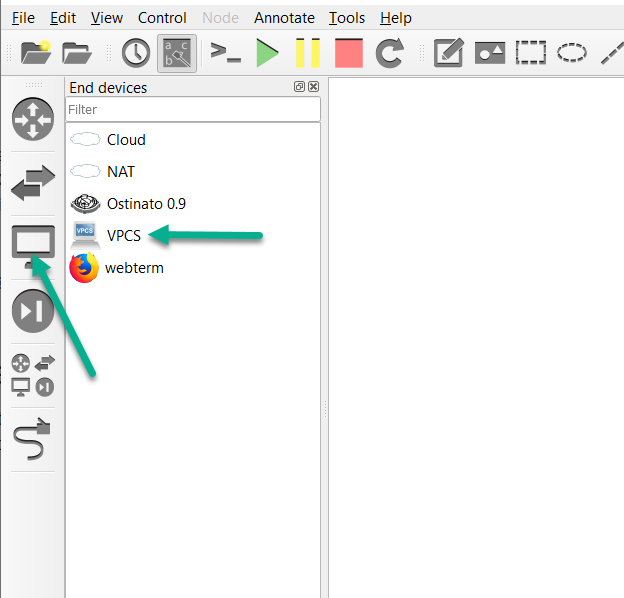
But VPCS can give you a big hand when you study the Cisco devices in the Dynamips. VPCS is not the traditional PC, it is just a program running on the Linux or Windows, and only few network commands can be used in it. You can ping/traceroute them, or ping/traceroute the other hosts/routers from the virtual PCs when you study


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
